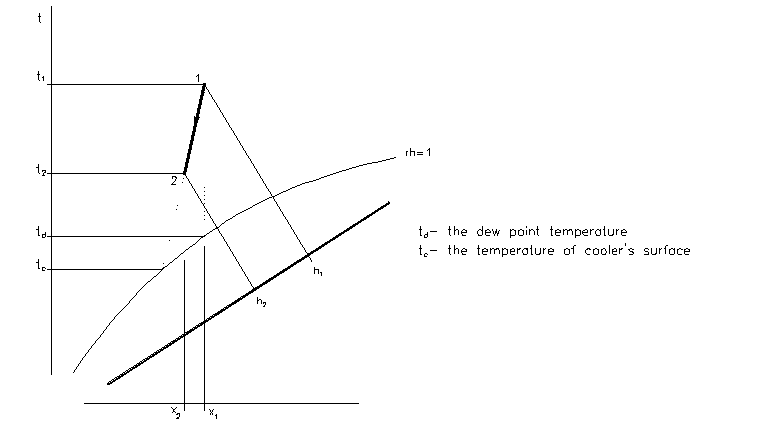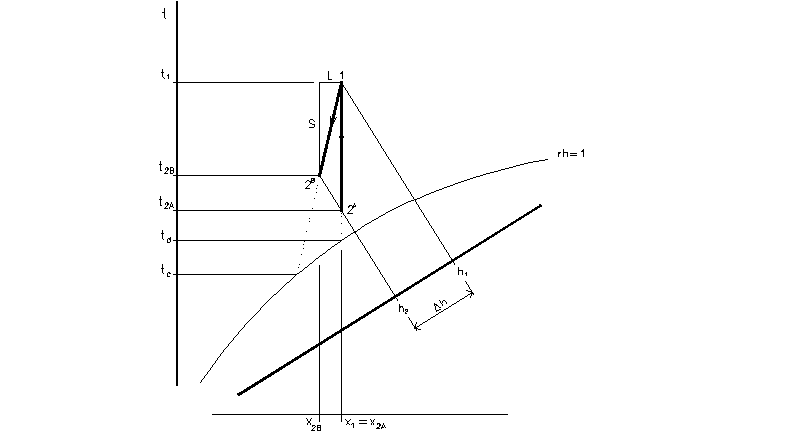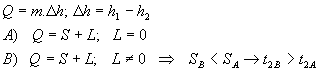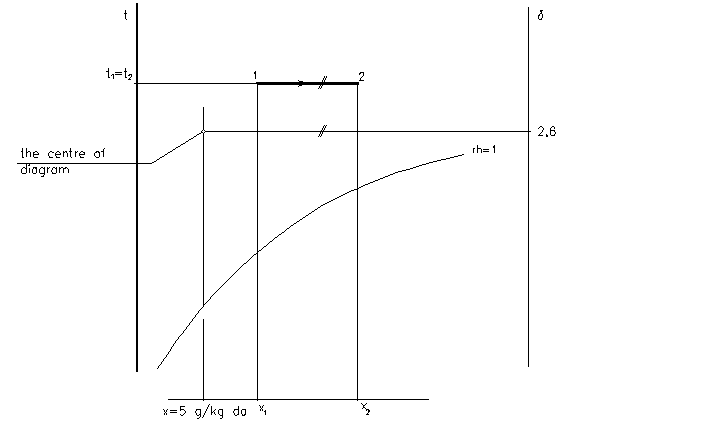What is Mollier’s chart?
- the tool for determining of isobaric psychrometric processes of moist air
- suitable for steady conditions
- similar to psychrometric chart used mainly in Anglo-Saxon literature
- each chart is determined for specific pressure
Description of the Mollier’s chart

Determination of the dew point temperature and the wet-bulb temperature
dew point temperature:
The temperature of moist air saturated at the same pressure p and with the same moisture content x as the given state of moist air.
thermodynamic wet-bulb temperature:
The temperature at which water evaporating into moist air, can bring air to the adiabatic saturation. The lowest temperature of adiabatic cooling of air.

Basic psychrometric processes
Introduction
- any process has two heat components
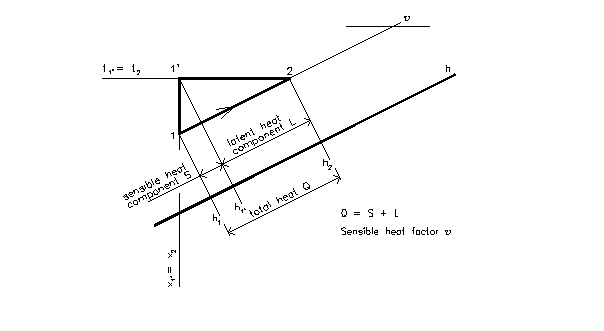
- sensible heat S – moisture is constant
- latent heat L – temperature is constant
1 – 2 is any process in Mollier’s chart
total heat Q = L + S
where:
latent heat component
L = ma.(h2 – h1’)
sensible heat component
S = ma.(h1’ – h1)
sensible heat factor u:
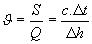
- ratio of sensible heat component included in total heat
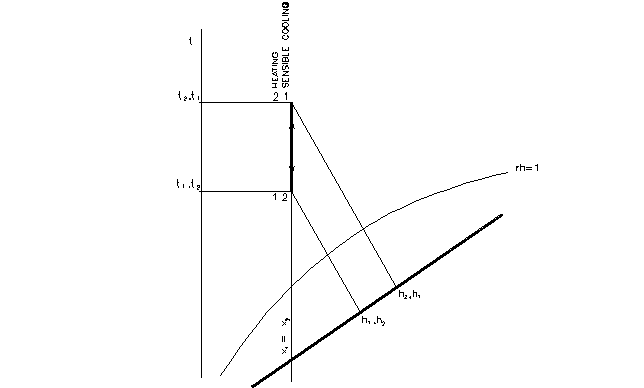
Sensible heating and cooling
- the process with no changes of moisture content x
- the sensible cooling and the sensible heating are reversed processes
- in the case of sensible cooling the surface temperature of cooler have to be higher than the dew point temperature of moist air
Properties of states:
x1 = x2
sensible cooling:
t2 < t1
rh2 > rh1
h2 < h1
heating
t2 > t1
rh2 < rh1
h2 > h1
Equation:
The heat required for the process:
sensible cooling:
Q = ma.(h1 - h2) = ma.cd.(t1 – t2) [kJ/s] = [kW]
heating
Q = ma.(h2 – h1) = ma.cd.(t2 – t1) [kW]
Cooling
- the process with change of moisture content x
- the surface temperature of cooler is lower than the dew point temperature of moist air -> the condensation occurs
Properties of states:
x1 > x2
t2 < t1
rh2 > rh1
h2 < h1
Equations:
The heat required for the process:
Q = ma.(h1 - h2) [kW]
The rate of condensing moisture:
mw = ma.(x1 – x2) [kg/s]
Mollier’s chart:
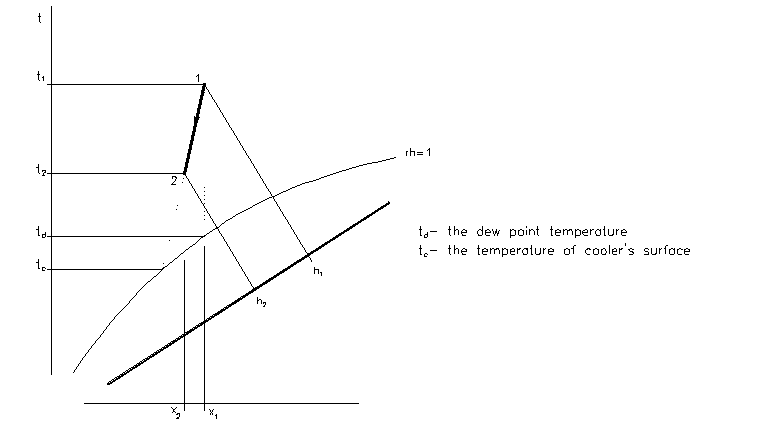
The different between sensible cooling and cooling
- while the cooler’s surface temperature is lower than the dew point temperature condensation of water vapour occurs -> a part of total heat is used for change from gaseous state to liquid state
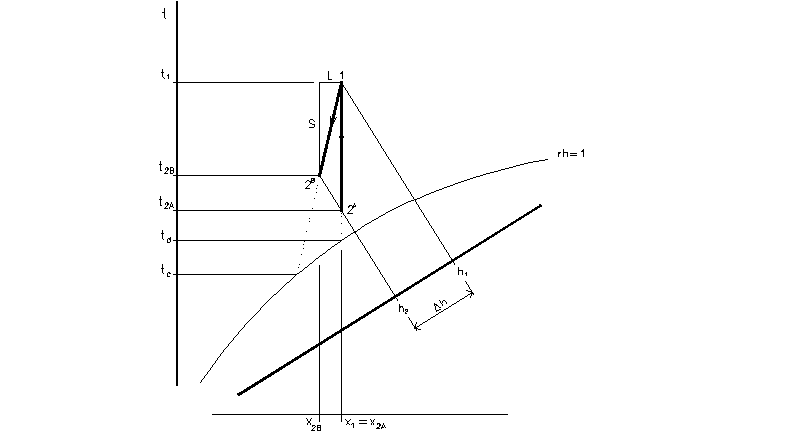
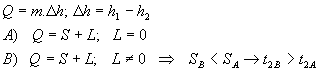
Humidification
- the moisture content can be increased in two ways
- the direct injection of steam into the air stream
- passing the air through a spray chamber containing small water droplets
a) Steam injection
Definition
the mass balance: ma1 = ma2 = ma
steady-flow energy equations:
ma.x1 + mv = ma.x2
ma.h1 + mv.hv = ma.h2
=> mv.hv = ma.( h2 - h1)
mv = ma.(x2 - x1)
Properties of states:
x1 < x2
t2 = t1
rh2 > rh1
h2 > h1
Mollier’s chart:
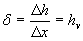
ratio d
where:
hv – specific enthalpy of injected steam (or any liquid)
hv varies about 2,6 kJ/kg
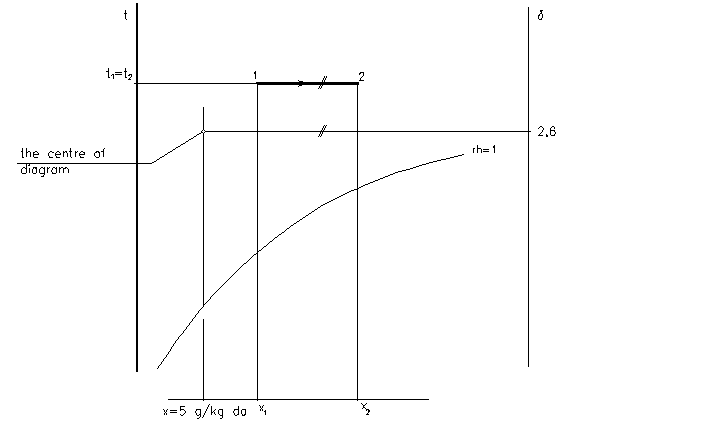
The process of steam injection in the air stream is taken with reasonable accuracy as isothermal.
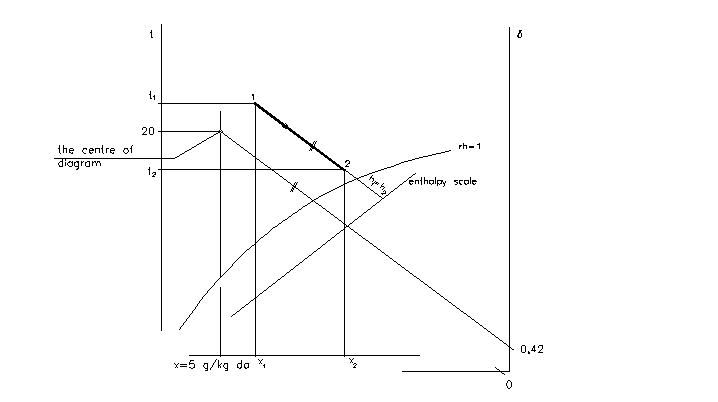
b) Humidification in spray chamber
Definition
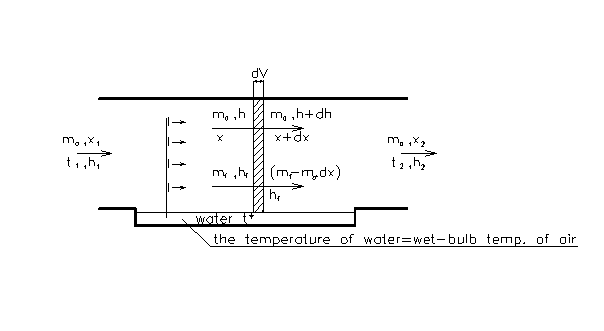
Energy balance:
ma.dh = ma.dx.hf
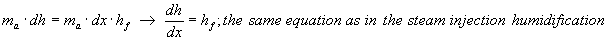
hf of water at temperature 10 to 15 °C varies between 0 to 0,42 kJ/kg
Properties of states:
x1 < x2
t2 < t1
rh2 > rh1
h2 = h1
Equations:
The rate of water transported into the air stream:
mw = ma.(x2 – x1) [kg/s]
Mollier’s chart:
Humidification with water in spray chamber is taken with reasonable precision as adiabatic => specific enthalpy is constant
Mixing
Definition
- mix of two air streams
steady-flow energy equation:
ma1.h1 + ma2.h2 = ma3.h3
mass balance equation:
ma1 + ma2 = ma3 for dry air
ma1.x1 + mva2.x2= ma3.x3 for water vapour
from the equations ensues:
Mollier’s chart:
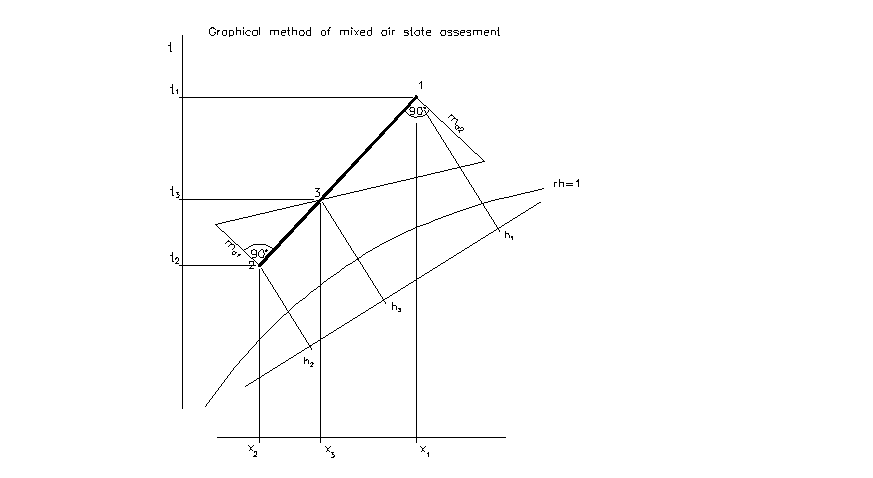
In the case of result state is below saturation curve:
state 3 is oversaturated air => air immediately changes to the saturated air according to the line of constant temperature, Dx is amount of condensed water steam.