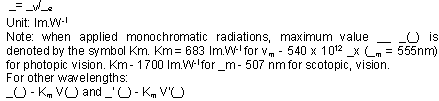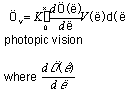-
Absolute
viscosity : the force per unit area required to produce unit
relative velocity between two parallel areas of fluid distance apart; also
called coefficient of viscosity .
-
Absolute zero temperature : the zero point on the Kelvin temperature
scale, (= -273.16oC)
-
Absorbent:
a material which extracts one or more substances form a liquid or gaseous
medium which it contacts and charges physically or chemically, or both (e.g.
soled absorbent: Calcium chloride, liquid absorbent: solutions of lithium
chloride, lithium bromide, and ethylene glycols).
-
Absorber:
an object absorbing another
object or radiation (e.g. the blackened surface within a solar collector,
which absorbs the solar radiation converting it to heat. These surfaces
usually absorb solar radiation but do emit a limmited amount of radiative
heat because of the so-called spectral selective coatings applied to the
surface).
-
Absorptance:
the ratio absorbed objects
or radiation. (For solar energy the ratio of absorbed to incident solar
radiation on a surface).
-
Absorptance
of a glazing material: in this context the absorption of solar
energy in the glazing material occurring throughout the thickness of a glazing
material. The absorptence is the fraction absorbed related to the incident
overall radiation (invoIving multiple reflections). The absorptence is different
for different wavelengths (coloured glazing) and angles of incidence. The
transmittance + absorptance + reflectance = 1.
-
Absorptance
of an opaque surface: the
ratio of the radiation absorbed at a surface relative to the incident radiation
on that surface. The absorptance is different for different radiation waveIengths
and angles of incidence. The absorptance of normally incident radiation
however is always numerically equal to the emittance of the surface for
the same wavelength. 'bIack body' is a theoretical perfect absorber with
an absorptance of 1 for all wavelengths: a typical matt black paint has
an absorptance of 0.97 for normal soIar radiation and 0.95 for long-wave
(thermal) radiation. For any wavelength and angle of incidence, for an opaque
surface, absorptance + reflectance = 1.
-
Absorption:
a process where an object
absorbs another object or radiation for example a process whereby a material
extracts one or more substances present in an atmospheric or mixture of
gases or liquids accompanied by the material's physical and/or chemical
changes.
-
Absorption
Factor: For solar
radiation the fraction of solar radiation, transmitted through a glazing
system that is absorbed inside the building.
-
Adaptive
model (adaptive approach): For
thermal comfort this is an approach to the study thermal comfort starting
from the observation that there are a range of actions which occupants can
take to achieve thermal comfort, and that discomfort is caused by constraints
imposed on the range of actions by social, physical or other factors (see
also Adaptive Principle). Over time this means that people are comfortable
at the 'usual' or 'average' temperature which they experience.
-
Adaptive
opportunity: For
thermal comfort: the ability of a building to allow adaptation to broaden
the band of temperatures at which the person could be comfortable. Actions
might include adding or removing a layer of clothing, changing posture,
or adjusting the metabolic rate. Spatial variation of temperature across
the room, availability of a desk fan, and the presence of sun shading or
openable windows would make the adaptive opportunities still greater. These
actions either alter the temperature which is required for comfort, or alter
the room temperature towards that which the occupants will find comfortable
-
Adaptive
Principle: A principle
which can be stated as: If a change occurs (in the thermal environment)
such as to produce discomfort, people react in ways which tend to restore
their comfort.
-
Adaptive
processes: The
range of actions that man takes to achieve thermal comfort.
-
Air
barrier: for buildings
a material carefully installed within a building envelope assembly to minimise
the uncontrolled passage of air into and out of a dwelling.
-
Air
change: One air change is an exchange of one volume of air equal
to internal volume of a room or building (see also Air Change Per Hour).
-
Air
changes Per hour (ach):
ventilation unit denoting the number of times a room exchanges its own total
air volume with outside air per hour. For the calculation of the air permeability
of a room or building this is determined (1) under natural conditions and
(2) under a 50 Pascal pressure difference. (The R-2000 Home Program requires
a house with 1.5 ach at 50 Pascal).
-
Air
conditioning: Control
of the indoor environment by controlling the thermal characteristics (cleaning,
changing the water content but mainly heating and cooling) the air supplied
to the room.
-
Air
leakage: the uncontrolled
flow of air for instance through a component of the building envelope, or
the building envelope itself, when a pressure difference is applied across
the component. Infiltration refers to inward flowing air leakage and exfiltration
refers to outward flowing airleakage.
-
Air
movement: the
movement of the air past a point, generally represented as the speed or
velocity of the air measured with an anemometer.
-
Air
permeability:
the property of a building component to let air pass when it is subjected
to a differential pressure.
-
Air
pressure: the
pressure exerted by the air. This may refer to static (atmospheric) pressure,
or dynamic components of pressure arising from air flow, or both acting
together.
-
Air
sealing: the practice
of sealing unintentional gaps in the building envelope (from the interior)
in order to reduce uncontrolled air leakage.
-
Air
tightness: the
degree to which unintentional openings have been avoided in a building's
structure.
-
Albedo:
The proportion of the global solar radiation that is reflected by the surface
of the Earth. Will clearly vary with materials and topography.
-
Altitude
angle: the angular height of above the horizon, i.e. the solar
altitude is the angle between the centre of the sun and the horizon.
-
Ambient
air: Generally,
the air surrounding an object or building.
-
Ambient
temperature: See: Air Ambient
-
Anemometer:
Instrument to measure the air speed; Common electrical types are hot wire
or and the hot-body anemometers. The principle used is to apply a fixed
electrical current to a wire and the voltage over the wire is measured.
The current heats the wire. Moving air cools the wire, decreasing the electrical
resistance. This change is measured through the voltage across the wire.
-
ANSI:
American National Standards
Institute
-
ASHRAE:
The American Society
of Heating Ventilating and Air-conditioning Engineers, based in Atlanta
Georgia, USA.
-
ASHRAE
scale: a set of
seven descriptors of subjective warmth. Usual wording is: Cold (-3), cool
(-2), slightly cool (-1), neutral (0), slightly warm (+1), warm (+2), and
hot (+3).
-
ASHRAE/ANSI
Standard 55: A
temperature standard proposed by the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration
and Air-conditioning Engineers formerly based on the Gagge's Standard Effective
Temperature, but due to come in line with ISO7730 (see below) in using Fanger's
PMV/PPD.
-
Attached
sunspace: -solar collector that doubles as useful building space
also attached greenhouse, solarium. The term 'attached' specifically implies
a space that shares one common wall with the associated building, such as
a conservatory.
-
Auxiliary
heating: the conventional (i.e. non-solar) contribution to the
total load (e.g. gas boiler etc.).
-
Awning:
an exterior, movable and usually flexible sun shading device. Protects by
deflecting or diffusing solar radiation at certain angles.
-
Azimuth
angle: The horizontal angle (in degrees) from the North point
measured clockwise. Thus North = 0o, East = 90o, South
= 180o etc.

-
Base
temperature: a fixed temperature in the definition of degree-days.
-
Beam
or direct radiation: the solar radiation directly from the sun
without changed angle or diffusion. Instruments for measuring direct radiation
require for practical reasons a wider aperture so the measured radiation
also contains radiation from the immediate region of the sky around the
sun (called circum solar; see also diffuse radiation).
-
Bedford
scale: A set of seven descriptors of subjective thermal response
from Much Too Warm (7), Too Warm (6), Comfortably Warm (5), Comfortable,
neither warm nor cool (4), Comfortably Cool (3), Too Cool (2), Much Too
Cool (1). This differs from the ASHRAE scale in defining the central three
categories as Comfortable.
-
Black
body: a perfect absorber and emitter of electromagnetic radiation
(light, heat etc). A black body absorbs all radiation without any reflection
(see also absorption). A cavity is a perfect black body. Lampblack is close
to a black body , while aluminium (polished) is a poor absorber and eminer
of radiation.
-
Bright
sunshine: sunshine above a certain level sufficient to be registered
on a Campbell-Stokes sunshine recorder .The threshold is imprecisely defined
and varies according to the type of recorder, but generally refers to sunshine
bright enough to cast a shadow. Burning typically starts when the beam intensity
is 200W /m2.g
-
BSI:
British Standards Institute
-
Building
orientation: Orientation of tihe building, generally used to
refer to solar orientation which is the siting of building with respect
to solar access. Although any building will have different orientations
for its different sides, the orientation can refer to a particular room,
or to the most important facade of the building.

- Calorific value:
the energy content per unit mass, per unit volume or released if reacting
with usualy oxigen (burned).
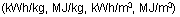
- Candela (cd) :
SI (Standard International) unit of luminous intensity: the candela
is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic
radiation of frequency 540 x 1012 hertz and has a radiant intensity in that
direction of 1/683 watt per steradian. (16th General Conference of Weights
and Measures, 1979)
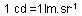
- Candela per square
metre (cd/m2): SI unit of luminance. (Note: this unit
was sometimes called the nit [nt] (name discouraged). Other units of luminance:
10-4 metric, non-SI: Lambert (L)

- Casual gain:
see internal gains
- CEN: The
European Standards Institution
- Chimney effect:
see stack effect.
- CIBSE:
The Chartered Institution
of Building Services Engineers.
- CIE Standard Overcast
Sky: completely overcast sky for which the ratio of its luminance
Ly in the direction at an angle X above the horizon to its luminance Lz at
the zenith is given by the relation Ly=Lz(1+2sinX)/3
- CIE standard sources:
artificial sources specified
by the CIE, whose radiations approximate CIE standard illuminants A, B and
C, (see CIE Publication N015).
- Clear sky (Standard):
cloudless sky for which the relative luminance distribution is described in
CIE Publication N022 (1973).
- Clear Sky:
Cloudless Sky - clear sky in this context has two separate meanings. In the
radiation Tables clear sky refers to days producing the mean maximum monthly
daily global radiation on a horizontal surface. These days on average contain
some cloud but the precise cloud amount is not known. In the temperature Tables,
the term clear skies refers to summaries of measured temperature data for
days when the mean total amount of cloud during hours of daylight was less
then 2/8.Night-time temperature data for such days are related to the same
'clear' days i.e. night-time cloud cover was not taken into account.
- Clerestory:
a window that is placed vertically (or near vertical) in a wall above one's
line of vision to provide natural light in a building.
- Climate chamber:
A chamber usually in a laboratory in which the environmental conditions can
be changed by the experimenter, used to investigate the effects of the thermal
environment on subjects.
- Climate
control : The
control of the indoor climate.
- Clo unit:
a unit for the insulating effect of clothing on a person. 1 clo = 0.155 (K.m2)/W.
- Clothing insulation:
The effective insulation of clothing worn characterized as a single layer
covering the whole body surface; measured in Clo Units or K.m2/W
- Clothing surface
temperature: Average
temperature of the surface of the clothes for use in heat exchange calculations.
- Colour rendering:
Effect of (not nescessarily white) light on the colour appearance of objects
compared to their colour appearance under a reference illuminant.
- Colour Rendering
Index (R): measure of the degree to which the psychophysical colour
of an object illuminated by the test illumihant conforms to that of the same
object illuminated by the reference illuminant, suitable allowance having
been made for the state of chromatic adaptation.
- Comfort chart:
a chart showing effective temperatures with dry-bulb temperatures and humidities
(and sometimes air movement), by which the effects of various thermal conditions
on human comfort may be compared.
- Comfort line:
a line on the comfort chart showing relation between the effective temperature
and the percentage of adults feeling comfortable.
- Comfort temperature
(neutral temperature): 1)The temperature (or environment)
judged by a population to be neutral on the ASHRAE scale, or Comfortable,
Neither Warm Nor Cool on the Bedford scale: assumed by most workers in the
field to be the desired temperature or
- 2) the temperature at which the greatest number
of people feel comfortable
- Comfort vote:
The subjective response
given by a subject on a comfort scale such as the ASHRAE or Bedford scales
(see above).
- Comfort zone:
The range of temperature within which a subject will feel comfortable, though
not necessarily neutral.
- Condensation:
condensed liquid - in this context beads, drops or a film of water (or frost)
that accumulates on the inside of facade elements, roofs or floors (usually
on windows) when warm, moisture air from the interior reaches a point where
the temperature (the 'dew point') no longer permits the air to sustain the
moisture it holds.
- Conduction:
the heat moving from a warmer to a colder region in the same substance without
mass transfer, this type of heat transfer depends on the thermal conductivity
of the material [measured in W/m2.K].
- Conductive heat
transfer : Process of conduction through a material. Materials
like copper or silver are good conductors.
- Constraints:
factors in the physical
or social environment which prevent people from taking actions to achieve
thermal comfort.
- Controlled ventilation:
ventilation brought about by mechanical means through pressure differentials
induced by the operation of a fan.
- Convection:
heat transfer between a surface and adjacent fluid (usually air or water)
and by the flow of fluid from one place to another. See also Forced convection,
Natural convection.
- Convective heat
transfer : Process of heat transport by convective flow. With free
convection the flow is caused by temperature differences is the liquid or
gas. For example the air inside double glazing transports heat due to natural
convection: the glazing layer on the inside is warmer than the one on the
outside; the air inside the cavity moves because of this temperature difference
and transports the heat. With forced convection energy is transferred due
to a mechanically driven gas flow or liquid flow.
- Convector:
an agency of convection. In heat transfer, a surface designed to transfer
its heat to a surrounding fluid largely or wholly by convection. The heated
fluid may be removed mechanically or by natural convection (gravity convector).
Such a surface may or may not be enclosed or concealed. Apparatus for heating,
in which the heat is passed on to the room by convection, due to natural air
movement sometimes helped by a fan.
- Cooling:
The process of active heat extraction for the benefit of climate control.
see also direct cooling, evaporative cooling, indirect cooling, regenerastive
cooling, surface cooling.
- Cooling effect,
sensible: difference between the total cooling effect and the dehumidifying
effect, usually in watts.
- Cooling effect,
total: difference between the total enthalpy of the dry air and
water vapour mixture entering the cooler per hour and the total enthalpy of
the dry air and water vapour mixture leaving the cooler per hour , expressed
in watts.
- Cooling element:
heat transfer surface containing refrigeration f1uid where refrigerating effect
is desired.
- Cooling load:
The thermal energy extracted from a building to maintain a pre-determined
indoor setpoint temperature.
- Cooling medium:
any substance whose temperature is such that it is used, with or without a
change of state, to lower the temperature of other bodies or substances.
- Cooling range:
in a water cooling device, the difference between the average temperatures
of water entering or leaving the device.
- Cooling water:
water for condensation of refrigerant; condenser water
- Core temperature
(deep body temperature):
The temperature of the internal organs of the body, especially the brain,
on the basis of which the thermoregulatory system of the body is controlled.
- Correlation::
An indication of the strength of the relationship between two variables characterised
by the correlation coefficient (r). The value of r varies between zero
(no relationship) and one (linear or exact relationship).
- Corresponding
values: values of parameters corresponding to other parameters.
- Counterflow:
flow in the opposite direction in heat exchange between two fluids; the coldest
portion of one meeting the coldest portion of the other.
- Critical temperature:
the saturation temperature corresponding to the critical state of the substance
at which the properties of the liquid and vapour are identical.
- Cross ventilation:
flow of air through a building caused by wind-generated pressure drop across
it.