Next to ventilation we can distinguish infiltration. Infiltration is an uncontrolled air exchange between indoor and outdoor through cracks and leakages in the facade. The consequence can be draught and energy loss. Because it is uncontrollable, in principle infiltration is undesirable.
Over the years buildings became more airtight for reasons of energy saving. Because we do need a basic amount of ventilation in a building, good ventilation possibilities become even more important in air-tight buildings.
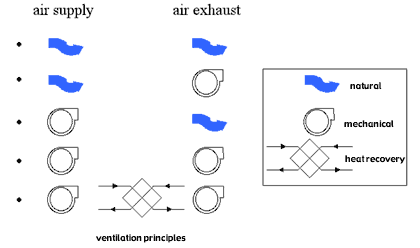
The supply and/or exhaust of ventilation air can be controlled naturally or mechanically: Natural supply and exhaust ; mechanical supply and natural exhaust ; natural supply and mechanical exhaust ; mechanical supply and exhaust . When the supply and the exhaust of the ventilation are controlled mechanically (balanced ventilation) a heat recovery system can be used. This way, warmth in the exhausted airflow is used to heat up the fresh airflow. The use of heat recovery saves a lot of energy. The energy use of a balanced ventilation system with heat recovery can easily be less than the energy use of a natural ventilation system, in spite of the lack of ventilator energy.
.